Projects
GeoScript Groovy
GeoScript Groovy is the Groovy implementation of GeoScript. GeoScript is a geospatial scripting API for the JVM that contains one API and four implementations (Python, JavaScript, Scala, and Groovy).
GeoScript is built on the shoulders of giants and essentially wraps the Java Topology Suite and the GeoTools libraries.
GeoScript provides several modules that includes geometry, projection, features, layers, workspaces, styling and rendering.
import geoscript.layer.Shapefile
import geoscript.geom.Bounds
def shp = new Shapefile("states.shp")
int count = shp.count
Bounds bounds = shp.bounds
shp.features.each {f->
println(f)
}
Geometry Commands
Github | Website | Presentation
Geometry commands is a command line library for processing geometry that follows the unix philosophy. Each command does one thing well (buffer, centroid, envelope) by reading in a geometry, processing the geometry, and writing the geometry out as WKT. Individual commands can be connected with unix pipes.
Geometry input with -g argument:
>>> geom buffer -g "POINT (10 10)" -d 2
Geometry input using standard input stream:
>>> echo "POINT (10 10)" | geom buffer -d 20
Piping results of one geometry command to another:
>>> geom buffer -g "POINT (10 10)" -d 2 | geom envelope
Determine if one geometry contains another:
>>> echo "POINT (0 0)" | geom buffer -d 10 | geom contains -o "POINT (5 5)"
true
>>> echo "POINT (0 0)" | geom buffer -d 10 | geom contains -o "POINT (25 25)"
false
geoc
Github | Website | Manual | Presentation
geoc is a geospatial command line application that follows the unix philosophy. Each command does one thing well (buffer a layer, crop a raster) by reading a vector layer as a CSV text stream or a raster layer as an ASCII grid, processing the layer or raster, and then writing out the vector layer as a CSV or a raster layer as an ASCII grid. Individual commands can be chained together with unix pipes.
geoc vector randompoints -g -180,-90,180,90 -n 100 > points.csv
cat points.csv | geoc vector buffer -d 10 > polygons.csv
cat points.csv | geoc vector defaultstyle --color navy -o 0.75 > points.sld
cat polygons.csv | geoc vector defaultstyle --color silver -o 0.5 > polygons.sld
geoc map draw -f vector_buffer.png -l "layertype=layer file=naturalearth.gpkg layername=ocean style=ocean.sld" \
-l "layertype=layer file=naturalearth.gpkg layername=countries style=countries.sld" \
-l "layertype=layer file=polygons.csv style=polygons.sld" \
-l "layertype=layer file=points.csv style=points.sld"
geo-shell
geo-shell is an interactive shell for geospatial analysis. It support vector, raster, and tile datasets and includes a map module. Behind the scenes it uses GeoScript Groovy, GeoTools, and JTS.
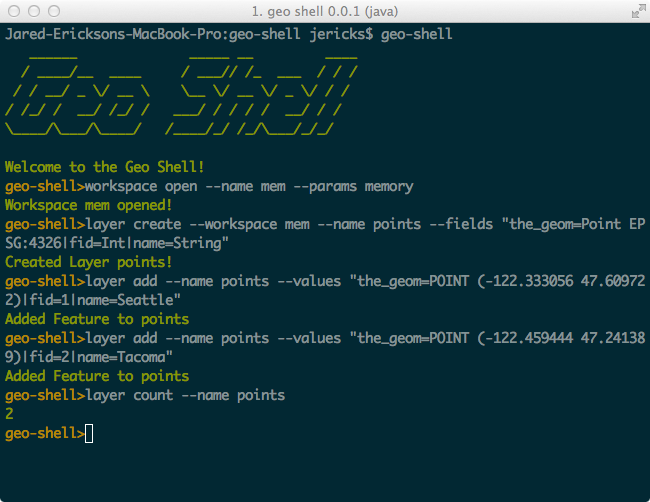
MBTilesServer
MBTilesServer is a Spring Boot and GeoScript microservice for serving your MBTiles map on the web with restful web services.
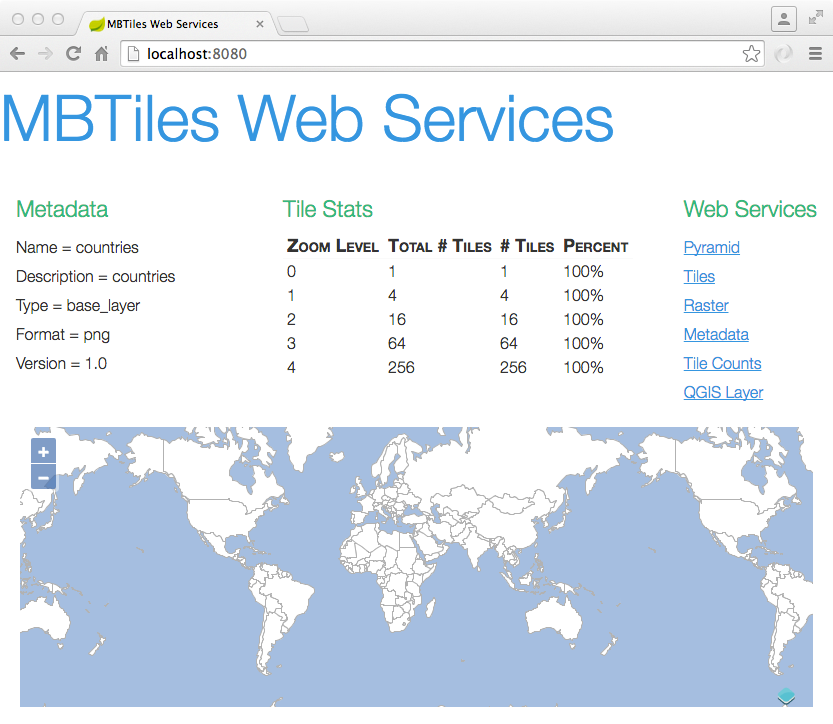
GeoPackageServer
GeoPackageServer is a Spring Boot and GeoScript microservice for serving your GeoPackage database on the web with restful web services.
Geometry Web Services
Geometry Web Services is a suite of micro geometry web services using the Java Topology Suite (JTS) and Micronaut written in Java.
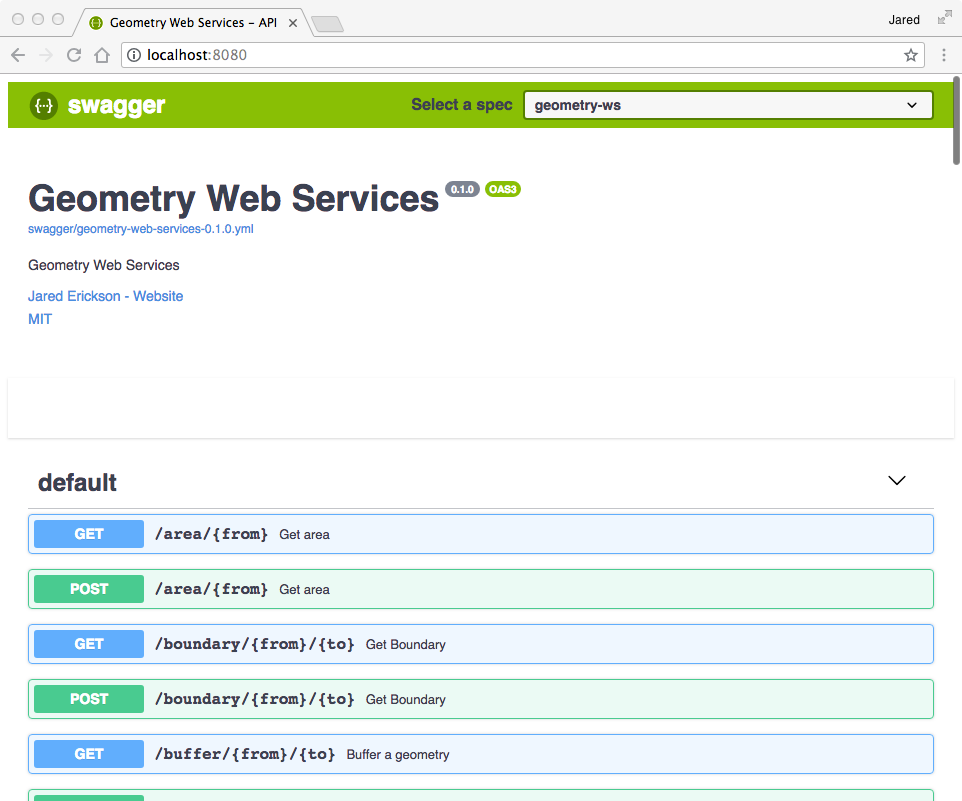
geos-cli
A Command line interface for GEOS - Geometry Engine Open Source.
Each command does one thing well (buffer, centroid, envelope) by reading in a geometry, processing the geometry, and writing the geometry out as WKT. Individual commands can be connected with unix pipes.
geos-cli buffer -g "POINT (1 1)" -d 10 | geos-cli centroid
geos-cli is written in C++ using CLI11 and GEOS. The Google Test library is used to write unit tests. The project is built with CMake and dependencies are managed with conan.
geos
GEOS is a C++ library for geometry. I added GeoJSON support.
You can now read a GeoJSON string.
geos::io::GeoJSONReader geojsonReader;
std::string geojson { "{\"type\":\"Point\",\"coordinates\":[-117.0,33.0]}" };
std::unique_ptr<geos::geom::Geometry> geom { geojsonReader.read(geojson) };
std::cout << geom->toText()) << "\n";
>>> "POINT (-117.000 33.000)"
And write a GEOS geometry.
geos::io::WKTReader wktReader;
std::unique_ptr<geos::geom::Geometry> geom(wktReader.read("POINT(-117 33)"));
std::string result = geojsonwriter.write(geom.get());
>>> {"type":"Point","coordinates":[-117.0,33.0]}
Python GDAL Cookbook
This cookbook has simple code snippets on how to use the Python GDAL/OGR API. The web site is a project at GitHub and served by Github Pages.
The cookbook started as a project at work and then expanded into a CUGOS project with lots of help from the community.
GeoServer Shell
Administer Geoserver using a command line interface (CLI). Geoserver Shell uses the same shell interface used by Spring Roo and provides extensive tab completion, history support, and the ability to run scripts.
Geserver Shell administers Geoserver using the excellent Geoserver Rest API. You can publish shapefiles, GeoTIFFs, and PostGIS layers, upload and download SLDs, and start tile seeding straight from the command line.
gs-shell>geoserver set --url http://localhost:8080/geoserver
gs-shell>workspace create --name naturalearth
gs-shell>shapefile zip --shapefile NaturalEarth/SmallScale/110m_cultural/110m_admin_0_countries.shp
gs-shell>shapefile publish --workspace naturalearth --file NaturalEarth/SmallScale/110m_cultural/110m_admin_0_countries.zip
ShapefileCpp
A C++ Shapefile API that wraps the C shapelib library.
shp::ShapefileReader shp {std::filesystem::absolute("points.shp")};
shp::Bounds b = shp.getBounds();
std::cout << "Bounds = " << b << "\n";
int numberOfFeatures = shp.getCount();
std::cout << "Number of Features = " << numberOfFeatures << "\n";
for(auto const& feature : shp) {
std:cout << f.getGeometry().wkt() << "\n";
}
MBTilesCpp
A C++ MBTiles API that can create MBTiles databases, load tiles and metadata but it cannot generate the content of tiles.
mbtiles::MBTiles mbtiles { "world.mbtiles" };
mbtiles.addTile(mbtiles::Tile(0,0,0,"tms/0/0/0.jpeg"));
mbtiles.addTile(mbtiles::Tile(1,0,0,"tms/1/0/0.jpeg"));
mbtiles.addTile(mbtiles::Tile(1,0,1,"tms/1/0/1.jpeg"));
mbtiles.addTile(mbtiles::Tile(1,1,0,"tms/1/1/0.jpeg"));
mbtiles.addTile(mbtiles::Tile(1,1,1,"tms/1/1/1.jpeg"));
mbtiles.tiles(1, [&](mbtiles::Tile& t) {
std::cout << t << "\n";
});
GeoPackageCpp
A C++ GeoPackage API.
const std::string fileName = "data.gpkg";
geopackage::GeoPackage geopackage { fileName };
std::string name = "basemap";
geopackage.createTileTable(name);
geopackage.addTile(name, geopackage::Tile(0,0,0,"data/tms/0/0/0.jpeg"));
geopackage.addTile(name, geopackage::Tile(1,0,0,"data/tms/1/0/0.jpeg"));
geopackage.addTile(name, geopackage::Tile(1,0,1,"data/tms/1/0/1.jpeg"));
geopackage.addTile(name, geopackage::Tile(1,1,0,"data/tms/1/1/0.jpeg"));
geopackage.addTile(name, geopackage::Tile(1,1,1,"data/tms/1/1/1.jpeg"));
geopackage.tiles(name, 1, [&](geopackage::Tile& t) {
std::cout << t << "\n";
});